An essential element in ensuring aseptic conditions is the
maintenance of HEPA filter integrity. Integrity testing should be
performed at installation to detect leaks around the sealing gaskets,
through the frames or through various points on the filter media.
Thereafter, integrity tests should be performed at suitable time
intervals for HEPA filters in the aseptic processing facility. For
example, such testing should be performed twice a year for the aseptic
processing room. Additional testing may be needed when air quality is
found to be unacceptable, or as part of an investigation into a media
fill or drug product sterility failure. Among the filters that should
be integrity tested are those installed in dry heat depyrogenation
tunnels commonly used to depyrogenate glass vials.
Saturday, December 22, 2012
Sunday, December 16, 2012
Vaccine manufacturing process
Vaccines
are a group of pharmaceuticals that include some of the oldest
biologically-made compounds. The Smallpox vaccine was introduced by Edward
Jenner as early as in 1796 and Louis Pasteur created the first live attenuated
bacterial (Chicken Cholera) and viral (Rabies) vaccines at the end of the 19th
century.
A vaccine contains an antigen that is capable of inducing an immune response in
a living organism and as such, typically enhances the organism’s ability to
fight off or minimize disease. These antigens can be live attenuated (weakened)
microorganisms such as in the MMR (Measles, Mumps, Rubella) virus vaccine,
inactivated microbes (bacteria, virus) or parts thereof (proteins,
polysaccharides) such as the DTaP (Diphtheria, Tetanus, acellular Pertussis)
vaccine.
Thursday, December 13, 2012
Filtration Technique
Filtration
is a common method of sterilizing drug product solutions. An appropriate
sterilizing grade filter is one which reproducibly removes all microorganisms
from the process stream, producing a sterile effluent. Such filters usually
have a rated porosity of 0.2 micron or smaller.
Whatever
filter or combination of filters is used, validation should include
microbiological challenges to simulate "worst case" production
conditions regarding the size of microorganisms in the material to be filtered
and integrity test results of the filters used for the study. The
microorganisms should be small enough to both challenge the nominal porosity of
the filter and simulate the smallest microorganism that may occur in
production. The microorganism Brevundimonas diminuta (ATCC 19146) when
properly grown, harvested and used, can be satisfactory in this regard because
it is one of the smallest bacteria (0.3 micron mean diameter).
Saturday, December 1, 2012
Part IV: Qualification of Water and Air Handling Systems
3. Steps of Validation
Validation plans
for water and air systems typically include the following steps:
1. Establishing standards for quality
attributes of water and air to manufacture pharmaceuticals.
2. Defining systems and subsystems suitable to produce
the desired water and air by considering the quality grades of water and
air.
3. Designing equipment, controls, and monitoring
technologies.
Tuesday, November 13, 2012
Part III: Qualification of Water and Air Handling Systems
1. Determination of Quality Attributes
In performing
the validation, defining the quality attributes—that is, gaining a clear
understanding of the required quality and intended use—is the most important issue,
and should be determined before starting the validation. Without defining
required quality attributes we cannot establish validation protocols, which are
the basis of all validation studies.
2. The Validation Protocol
A validation
protocol is defined as
"A written plan stating how validation will be
conducted and defining acceptance criteria. For example, the protocol for a
manufacturing process identifies process equipment, critical process
parameters/operation ranges, product characteristics, sampling, and test data
to be collected, number of validation runs, and acceptable test results."
Part II: Qualification of Water and Air Handling Systems
A. Validation Concept
To prove the performance,
one must demonstrate (document) that the processes or systems consistently
produce the specified quantity and quality of water and/or air when operated
and maintained according to specific written operating and maintenance procedures.
In other words, validation involves proving
1. Engineering
design
2. Operating
procedures and acceptable ranges for control parameters
3. Maintenance
procedures
To accomplish
this, the system must be carefully designed, installed, and tested during and
after construction, and therefore for a prolonged period of time under all
operating conditions.
Saturday, November 10, 2012
Recent Facts of Indian Pharma Industry
SMS service for awareness on cheaper drugs:
Sep 1, 2012, 12.59PM IST, The writer has posted comments on this article PTI
NEW
DELHI: The Department of Pharmaceuticals in the Ministry of Chemicals
and Fertilisers is planning to launch a SMS service providing
information about affordable alternatives to medicines prescribed by
doctors.The Short Message Service (SMS) facility could help poor
patients find cheaper alternatives to medicines prescribed by doctors.
The
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has sought that all 348 drugs
listed in the National List of Essential Medicines, 2011 should be
brought within the purview of the Drug Price Control Order (DPCO) so
that there should be minimum impact on the expenses of consumer.
Friday, November 9, 2012
Part I: Qualification of Water and Air Handling Systems
High-quality
water and air are essential for the manufacture of pharmaceuticals. Water is
the most commonly used raw material in pharmaceutical manufacturing; it is
indirectly used in the manufacture of all dosage forms for cleaning manufacturing
equipment, and is also used as a major component which constitutes injectable
products. It is the one raw material that is usually processed by the
pharmaceutical manufacturer prior to use because it cannot be used as supplied by
the vendor. Water should be regarded as one of major raw materials for the
manufacture of pharmaceuticals whether or not it remains as a component of the
finished dosage form or is eliminated during the manufacturing process. Water
is thus an important raw material in GMP and in validating the manufacturing process.
Thursday, November 8, 2012
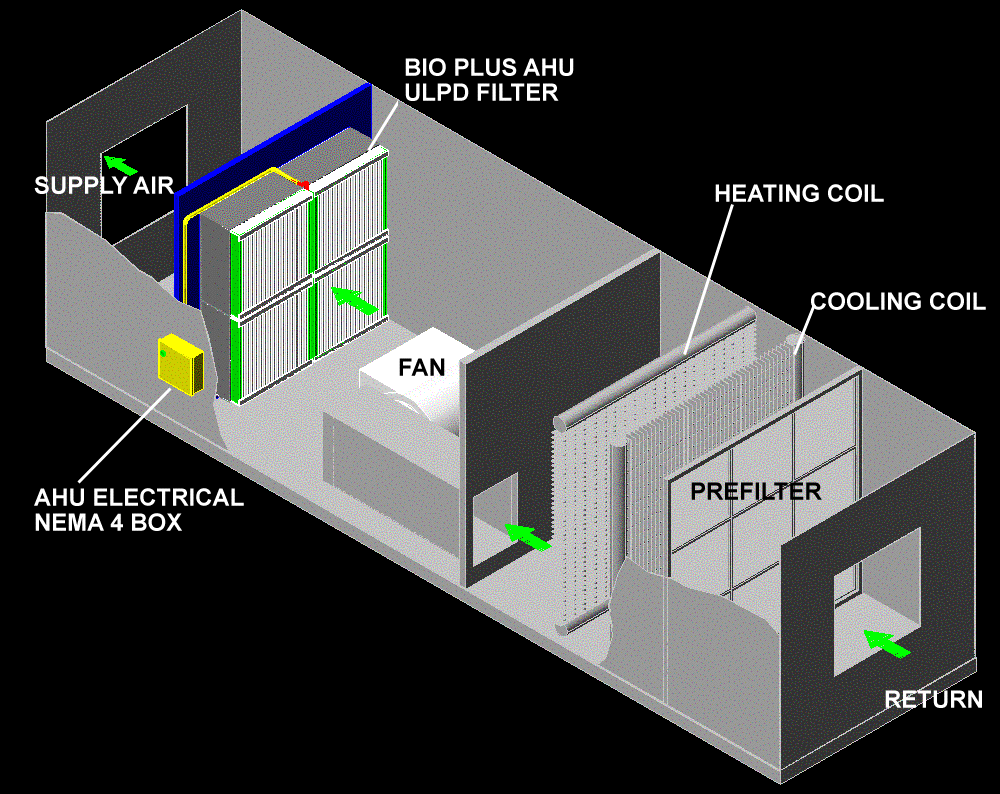
Brief Idea On HVAC System
Introduction:
Heating,
ventilation and air-conditioning (HVAC) play an important role the
manufacture of quality pharmaceutical products. A well designed HVAC
system will also provide comfortable conditions for operators. HVAC
system design influences architectural layouts with regard to items such
as airlock positions, doorways and lobbies. The architectural
components have an effect on room pressure differential cascades and
cross-contamination control. The prevention of contamination and
cross-contamination is an essential design consideration of the HVAC
system.
About HEPA filters used in HVAC system
About HEPA (High efficiency particulate air)
High-Efficiency Particulate Air or HEPA
is a type of air filter. It is a type of filter which has high
efficiency to filter out about 99.997% that is why they are termed as
High efficiency particulate air filter,HEPA filters are made up of a
mesh of fiber glass fibers of thickness ranging from 0.5 to 2 micrometer
and are closely packed with each other with as low clearance as 0.3μm
which may be bit greater.
Particles in air are trapped in to HEPA
filter fibers when air caring these particles is blown or passed through
these fibers, by mechanism of interception (particles adhere to
fibers), impaction (particles embed in to the gap) and diffusion and
then blocking, particles with lower particle size than the gap between
these fibers are also trapped as the result above mechanisms fiber
diameter, filter thickness, and face velocity are the factors which
affect the efficacy of the HEPA filter.
Guide To Inspections Validation Of Cleaning Processes
I. INTRODUCTION
This article is written to guide and design how
to set up validation procedure, one must recognize that for cleaning
validation, as with validation of other processes, there may be more than one
way to validate a process. In the end, the test of any validation process is
whether scientific data shows that the system consistently does as expected and
produces a result that consistently meets predetermined specifications.This guide is intended to cover equipment cleaning for chemical residues
only.
Monday, November 5, 2012
Brief Introduction Of ICH Guidelines
The International Conference on Harmonisation of Technical Requirements for Registration of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) is a project that brings together the regulatory authorities of Europe, Japan and the United States and experts from the pharmaceutical industry in the three regions to discuss scientific and technical aspects of pharmaceutical product registration.
The purpose of ICH is to reduce or obviate the need to duplicate the testing carried out during the research and development of new medicines by recommending ways to achieve greater harmonisation in the interpretation and application of technical guidelines and requirements for product registration. Harmonisation would lead to a more economical use of human, animal and material resources, and the elimination of unnecessary delay in the global development and availability of new medicines while maintaining safeguards on quality, safety, and efficacy, and regulatory obligations to protect public health.
Saturday, November 3, 2012
Cleanroom Classification and Examples for Working Steps According to EU GMP Guide
Cleanroom Classification
The current demands in today’s pharmaceutical
industry for quality control and quality assurance have been driven by the
aspiration to deliver consistently high quality and safe products to the
consumer. The standards that are set to meet this goal are exorbitant and
tightly controlled both internally and externally.
Cleanroom environments are a crucial area for
the process and manufacture of pharmaceutical products. Cleanrooms are
controlled and maintained using very stringent protocols and guidelines
outlined by different organization. To monitor the quality of a room, proper standards
have to be established. Different room
classes are necessary for the different production areas as regards the different
production steps.
Thursday, November 1, 2012
Major Drug Regulatory Agencies World Wide
Pharmaceutical companies and regulatory agencies work together to
enhance patient safety when a medicine is first being studied
(pre-approval) and after it becomes available to patients and their
health care providers as a treatment option, following authorization by
regulatory agencies (post-approval).
Regulatory agencies are government or non-government authorities,
responsible for oversight of the effectiveness, safety, manufacture, and
distribution of medicines in a specific country or region of the world
such as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and European
Medicines Agency (EMA).
Every country has its own regulatory authority, which is
responsible to enforce the rules and regulations and issue guidelines for drug development,
licensing, registration, manufacturing, marketing and labeling of
pharmaceutical products.
Writing Standard Operating Procedures (SOP)
1.0 Overview
A Standard
Operating Procedure (SOP) is a set of written instructions that document a
routine or repetitive activity followed by an organization. The development and
use of SOPs are an integral part of a successful quality system as it provides
individuals with the information to perform a job properly, and facilitates
consistency in the quality and integrity of a product or end-result.
The term “SOP” may not always be appropriate
and terms such as protocols, instructions, worksheets, and laboratory operating
procedures may also be used. For this document “SOP” will be used. This
document is designed to provide guidance in the preparation and use of an SOP
within a quality system.
Implementation Of Change Control
Change control is defined as :
“A formal system by which qualified representatives of appropriate disciplines
review propose or actual changes that might affect a validated status. The
intent is to determine the need for action that would ensure and document that
the system is maintained in a validated state.”
The implementation of a change
control system is an important and necessary step in the validation approach
for equipment and facilities. Vital to any change control system is its
efficiency in that it does not require too much time and effort to handle
changes.
Application Of The F0 Value in Steam Sterilizer
The F0
value of a saturated steam sterilisation process is the lethality expressed in
terms of the equivalent time in minutes at a temperature of 121 °C delivered by
the process to the product in its final container with reference to micro-organisms
possessing a Z-value of 10. The total F0 of a process takes
account of the heating up and cooling down phases of the cycle and can be
calculated by integration of lethal rates with respect to time at discrete temperature
intervals. When a steam sterilisation cycle is chosen on the basis of the F0
concept, great care must be taken to ensure that an adequate assurance of
sterility is consistently achieved. In addition to validating the process, it
may also be necessary to perform continuous, rigorous microbiological monitoring
during routine production to demonstrate that the microbiological parameters
are within the established tolerances so as to give an SAL of 10^−6 or better. In
connection with sterilisation by steam, the Z-value relates the heat
resistance of a micro-organism to changes in temperature.
Basic Check Points Of Autoclave Validation
The success of sterilization is
dependent upon the performance reliability of the autoclave. Validation of
effectiveness includes monitoring temperature, pressure and cycle duration time
for each cycle and providing periodic sterilization/decontamination challenges
(quality assurance), i.e. use of biological indicators. A logbook should be
maintained to record autoclave use and be available for inspection.
Wednesday, October 31, 2012
Component Of Master Validation Plan
1. Introduction
1.1 Project Description
1.2 What a Validation Master Plan Is
1.3 Scope of Validation Master Plan
1.4 Definition for the Term Validation
1.5 Validation Team Member
1.6 Validation Team Responsibility
2. Concept of Qualification or Validation
2.1 Fundamentals
2.2 Concept of a Validation Life Cycle
2.3 Elements of Validation
2.4 Documentation Format of Qualification Programs
2.5 Numbering System
Basic Concept Of Validation
1. Definition of Validation
- Action of proving, in accordance with the principles of good manufacturing practice, that any procedure, process, equipment, material, activity, or system actually leads to the expected result
- Documented evidence which provides a high degree of assurance that a specific process will consistently produce a product meeting its predetermined specifications and quality attributes and characteristics
- Obtaining and documenting evidence to demonstrate that a method can be relied upon to produce the intended result within defined limits
- Action to verify that any process, procedure, activity, material, system, or equipment used in manufacture or control can, will, and does achieve the desired and intended results.
Interview Questions for Pharmaceutical industry related jobs (QA,QC,Production,RA,f&d) for B.pharma /M.pharma (Part 1)
Interview questions mostly asked during technical round in Production :
01. Q. Which type of tablets are exempted from Disintegration testing?
A. Chewable Tablets
Cleaning Validation And Its Importance In Pharmaceutical Industry
Pharmaceutical manufacturers must
validate their cleaning process to ensure compliance with cGMP regulations.
Minimizing equipment downtime has the potential to impact the efficiency and
economics of pharmaceutical production. The main purpose of cleaning validation
is to prove the effectiveness and consistency of cleaning in a given
pharmaceutical production equipment to prevent cross contamination and
adulteration of drug products with other active ingredients like unintended
compounds or microbiological contamination, leads to prevent several serious
problems and also useful in related studies like packaging component cleaning
validation. So it is necessary to validate the cleaning procedures to ensure
safety, efficacy, quality of the subsequent batches of drug product and
regulatory requirements in Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (API) product
manufacture. The benefits due to cleaning validation are compliance with
federal regulations, identification and correction of potential problems,
previously unsuspected which could compromise the safety and efficacy of drug
products. In this article cleaning, validation and importance are discussed in
brief
Steam Quality Parameters And Effects Of Their Deviations From Accepted Values
Steam Dryness:
The measure of the water content of steam deliverd to the sterilizer chamber.Acceptable values are 0.9 or greater (<10% water) for non-metallic loads and 0.95 or greater (<5% water) for metallic loads.
Wet steam can cause an unsterile load in two ways:
- Insufficient energy delivered to the load to sterilize.
- “wet packs”, making the sterile barrier material surrounding the load less of a barrier and compromising sterility assurance.
Steam Purity Checks Before Start Sterile Operation In Biopharmaceutical Industries
In the pharmaceutical manufacturing and health-care industries, there are basically two types of steam–process steam and pure steam.
Process steam is also known as plant steam, black steam, utility steam,
boiler steam etc. Pure steam is sometimes known as clean steam.
Process steam is defined as a general
purpose steam whose quality is not been optimised for sterilisation.
Where it is not intended to be in direct contact with medical devices,
medicinal or culinary products, no specific physical, chemical or
biological contamination limits are set. The steam may contain various
volatile additives (such as those intended to inhibit corrosion in
condensate return pipes) which are unacceptable for topical or
parenteral administration to human beings.
7 steps of Corrective Action Preventive Action (CA-PA)
CAPA
(Corrective Action Preventive Action) and failure investigation become
more and more important for the pharmaceutical industry. This becomes
clear in a series of guidance documents. Above all with the ICH Q10
document, CAPA was introduced as a new quality-assuring tool. This
document states e. g. that a pharmaceutical company should have a system
in place for taking corrective and preventive measures (CAPA). These
can, among other things, result from complaints, deviations, recalls,
observations in audits and inspections or monitoring results. The
investigations within the system should aim at finding the actual cause.
The outcome should be that process and product are better understood
and improvements are derived.
Quality Assurance(QA) role In Pharma Industry
Technology Transfer :
- Receipt of product design documents from Research Center.
- Distribution of documents received from Research Center (RC).
- Checking & approval of documents generated based on RC documents i.e. Batch Manufacturing Record.
- Scale-up and validation of product
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
Featured Post
Complication in Pharma industry with stability issue and salary expectation in Indian scenario
Now a days the pattern of interview is very interesting in pharma industry. The main argument comes with following points, Exp...

-
C urrent regulatory inspection is come up with lots of recommendations. In this article will be discussing regarding the different regulat...
-
I solators have been around the Pharmaceutical Industry since the early 1980s and in the Nuclear Industry (glovebox technology) since the...
-
The initial qualification must demonstrate that the sterilization process is robust, consistent, and capable of achieving a Sterility Assu...